What is cold Forging? Features and Main Products
What is Hot Forging? Features and Main Products
Difference between Cold Forging and Hot Forging
Cold forging that only we can do
Examples of our cold forged products
Leave it to us to design and manufacture cold forgings!

Cold forging (also called cold heading) is a plastic forming process in which pressure is applied to a metal material at room temperature. When metal is deformed by applying pressure beyond a certain level, it has a property of not returning to its original shape, and this property is called plasticity (deformation due to plasticity is called plastic deformation). Conversely, if a metal returns to its original shape when pressure is applied to deform it and then pressure is removed, this deformation is called elastic deformation.
In cold forging, it is first necessary to design and fabricate a die to form the desired part. The material of the die is often tool steel or high-speed steel (HSS). In general, if a cold heading machine such as a cold header or parts former is equipped with a die, basically all processes from cutting to finishing of coil-shaped materials can be performed on a single heading machine. However, there are cases where special secondary processes such as cutting, grinding, and tapping are required.
Cold forging has three main characteristics: 1) it is a plastic process, so unlike cutting, there is little material loss; 2) the material is at room temperature, so there is almost no dimensional change due to temperature change, and high precision can be achieved; and 3) (for the same reason as in 2) near-net-shape and net-shape processing can be performed, so secondary processing is not required and costs are reduced.
Again, in cold forging, the deformation resistance is greater than in hot or warm forging because the material is at room temperature. Therefore, many of the products manufactured by cold forging are relatively small, and the disadvantage is that the dies are prone to wear and tear. Typical products include screws, bolts, nuts, collars, and washers.
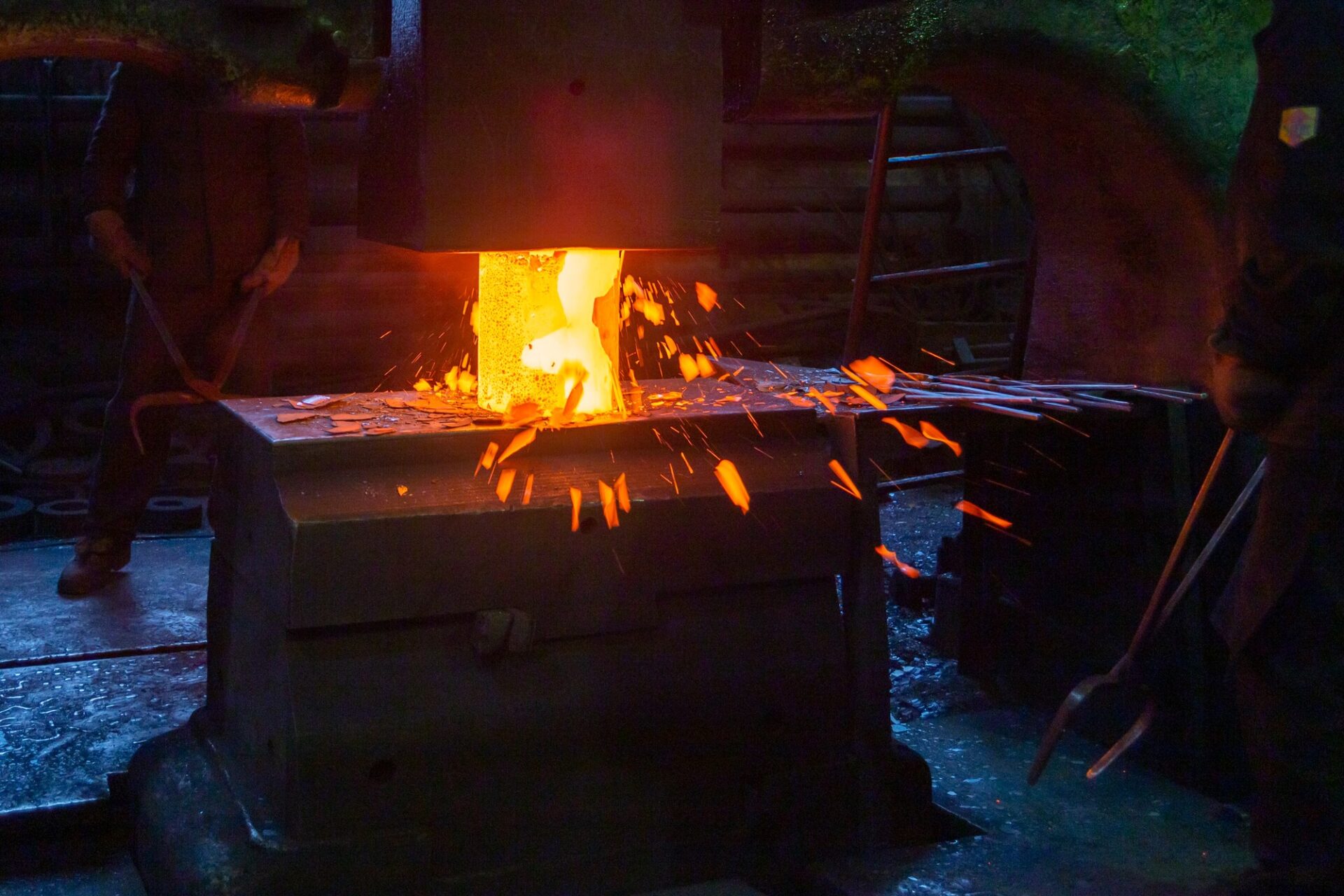

The following is a detailed explanation of hot forging. Hot forging is a forging process in which the material is heated to a recrystallization temperature of approximately 900°C to 1,200°C or higher, depending on the material, before being formed. For iron, the appropriate temperature for hot forging is about 1,100 to 1,250℃, and for brass, about 700 to 750℃.
The advantage of hot forging is that the metal material is heated to a high temperature, so the deformation resistance of the material is relatively low and large parts that would be difficult to form by cold forging can be processed. On the other hand, the disadvantage is that the accuracy, including dimensional tolerance and surface roughness, is inferior to cold forging due to the large dimensional change of the workpiece caused by temperature change. In addition, since annealing is required to remove internal stress (distortion), the cost of secondary processing can be a bottleneck.
The products manufactured by the process of hot forming are various many kind,like high pressure valve and pomp,cylinder, industrial machine parts. As we mentioned, the most of them are large parts comparatively.
The table below summarizes the differences between cold forging and hot forging.
| processing method | Cold Forging | Hot forging |
| Temperature | normal or average or fixed temperature | 900-1,200°C (above recrystallization temperature) |
| feature | High deformation resistance Small dimensional change | Low deformation resistance Large dimensional change and poor accuracy after machining |
| Advantages | High accuracy can be achieved. | Capable of processing large items |
| Disadvantages | Molds are prone to wear and tear | Secondary processing is required, which is costly. |
| Main Products | Relatively small screws, bolts, nuts, washers, etc. | Relatively large high-pressure valves, pumps, cylinders, etc. |
As shown in the table above, the key point is to choose cold forging when high precision is required for small products and hot forging when mass production of large products is desired.
However, it may vary depending on the product type, material, shape, required accuracy, etc. Please consult with a specialist first.
The first is in-house production of die design and fabrication using 3D CAE analysis with our CAE software “Deform 3D”. The second is a production system that enables high value-added and high-speed mass production of products, backed by more than 100 machining facilities, including Japan’s most multi-stage 9-stage parts former. Third, we have a track record of 130 VA/VE proposals per year.
Thanks to these three strengths, we have long been supported by customers in various industries, including the automotive, light electrical appliance, home appliance, and housing industries, as a professional cold forging company.
Here are some examples of our cold forged products.


>>Click here for more product examples
Our company, Arai Parts, specializes in the design and manufacture of cold forged products. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about the design and manufacturing of cold forged products. Online business meetings and factory tours are also available upon request.
Cold Forging/VA/VE CenterTo contact the Cold Forging/VA/VE Center,
Please contact us by Tel or by filling out the inquiry form.
If yo uare in a hurry, please give us a call.